Sealless Pump - Types, Applications, Advantages and Limitation
🔗Hermetic, semi-hermetic and open compressor
🔗Working of Electromagnetic clutch
What is a sealless pump? What is their importance?
Some pump applications require zero product leakage, even less than the minimal leakage possible from a well-chosen and well-maintained mechanical seal. Zero leakage is essential while handling toxic liquid. Most emissions are caused by leakages in pumps used in the industry. A number of stringent environmental and safety regulations force the industry to adopt methods that reduce or eliminate fugitive emissions in the workplace.
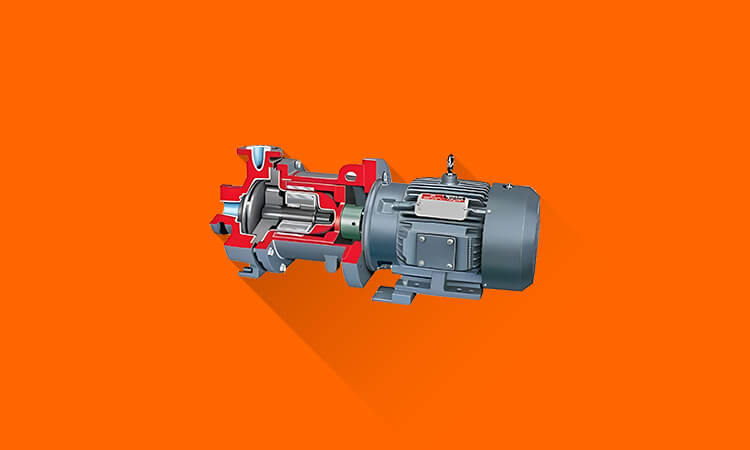
Sealless pump design eliminates the need for the dynamic shaft seal between a wetted end of a centrifugal pump and an atmosphere. A sealless pump has a fully enclosed wet end, eliminating any need for a seal and preventing the possibility of material leakage. Instead of a single shaft running from the motor to the impeller, the shaft comprises two separate pieces. One piece is powered by a motor on the dry end, while the other piece drives an impeller on the fully enclosed wet end. Both shaft pieces are coupled magnetically.
Types of sealless pumps
The two most common types of sealless pumps used in industry are magnetic drive and canned motor types. These two types of pumps differ in how they get their power from the motor. Both pumps feature a fully contained pump housing without any physical attachment between the motor drive shaft and the pump shaft. It eliminates the need for a shaft seal, which means there is no potential for seal leakage.
Magnetic drive pumps use separate, standard motors coupled to the internal pump drive via synchronous magnetic couplings made of neodymium iron or samarium cobalt. The drive in a canned motor is integral within the pump housing, with the stator and rotor of an AC electric motor separated from the pumped liquid by a nonmagnetic membrane. Both technologies have been around for many years, but both are continuing to be improved to higher horsepower levels, operating temperatures and with aggressive liquids.
🔗Difference between magnetic drive pump and canned motor pump
Applications of sealless pump
Sealless pump is used where the handling of liquid must be leak-free. The following applications would not usually be tolerated with even the slightest amount of leakage: Radioactive liquids, Toxic liquids (e.g., phosgene, cyanide), Carcinogens, Noxious, malodorous liquids, highly corrosive liquids, Hot liquids (e.g., heat transfer liquids) etc.
Sealless pumps are also preferable, where a mechanical seal would be expensive to buy and maintain.
Advantages of sealless pump
Properly designed and applied sealless pumps may offer the following advantages:
- Eliminated leakage of primary containment material into the environment during normal operation.
- Ensure safety when handling hazardous liquids.
- Prevented the loss of expensive liquids.
- The axial thrust is unaffected by suction pressure.
- Reduces noise levels.
- Eliminated periodic maintenance and replacement costs for shaft seals.
Disadvantages of sealless pump
Here is some limitation of sealless pump.
- The primary containment shell is relatively thin and should be considered when assessing corrosion potential.
- The heat is generated by motor windings or magnet components.
- Drive section overheating may occur with loss of flow or loss of suction. Drive-generated heat may affect the required NPSH for some circulation plans for volatile liquids.
- The cost of repair can be higher if bearings fail before detection. It may be necessary to retrain maintenance personnel.


.jpg)