Elements of Plain Milling Cutter - Nomenclature and Angles
Read: What Is Milling Operation?
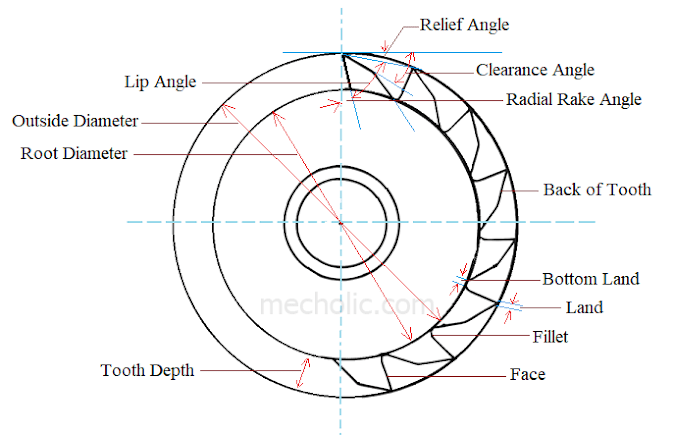
A milling cutter can be considered as the cluster of single point cutting tool. Above figure shows a plain milling cutter. The various parts of milling cutter teeth are cutting edge, face, filling, and body. The teeth of milling cutter either straight (the cutting edge is parallel to the axis of rotation) or helical shaped.
Periphery: It is defined as the locus of cutting edges of tooth of cutter.
Cutting edge: It is the portion that touches the workpiece during cutting action. It is the intersection of teeth face and tooth flank.
Fillet: portion where one teeth joins the face of another tooth. It is a reinforcement to cutting tooth.
Face of teeth: it is the surface upon the chip is formed while cutting. It may be curved or flat.
Back of tooth: it is the created by fillet and the secondary clearance angle.
Land: it is the narrow surface on the back of cutting edge. Land is the result of providing the clearance angle.
Bottom Land: the blank space between the consecutive teeth.
Root diameter: diameter passing through centre of cutter and joining two ends of the periphery.
Root diameter: passing through centre of cutter and joining two bottom fillet.
Relief angle: it is the angle between the tangent to the outside diameter of the cutter at cutting edge and the land of the tooth. The function relief angle is to avoid the interference between the land of the tooth and the work surface. The relief angle varies with the type of material to be machined.
Radial rake angle: it is the angle between the face of teeth and the radial line passing through the cutting edge of the tooth. The radial rake angle may be positive, negative or zero. It is provided free cutting by allowing chips to flow smoothly on the face of the cutter.
A milling cutter can be considered as the cluster of single point cutting tool. Above figure shows a plain milling cutter. The various parts of milling cutter teeth are cutting edge, face, filling, and body. The teeth of milling cutter either straight (the cutting edge is parallel to the axis of rotation) or helical shaped.
Elements of plain milling cutter
Body of cutter: It is the main frame of milling cutter, on which the teeth rest.Periphery: It is defined as the locus of cutting edges of tooth of cutter.
Cutting edge: It is the portion that touches the workpiece during cutting action. It is the intersection of teeth face and tooth flank.
Fillet: portion where one teeth joins the face of another tooth. It is a reinforcement to cutting tooth.
Face of teeth: it is the surface upon the chip is formed while cutting. It may be curved or flat.
Back of tooth: it is the created by fillet and the secondary clearance angle.
Land: it is the narrow surface on the back of cutting edge. Land is the result of providing the clearance angle.
Bottom Land: the blank space between the consecutive teeth.
Root diameter: diameter passing through centre of cutter and joining two ends of the periphery.
Root diameter: passing through centre of cutter and joining two bottom fillet.
Angles of milling cutter
Lip angle: It is the angle between the face of the teeth and the land of the teeth. Land is a narrow surface on the back of teeth.Relief angle: it is the angle between the tangent to the outside diameter of the cutter at cutting edge and the land of the tooth. The function relief angle is to avoid the interference between the land of the tooth and the work surface. The relief angle varies with the type of material to be machined.
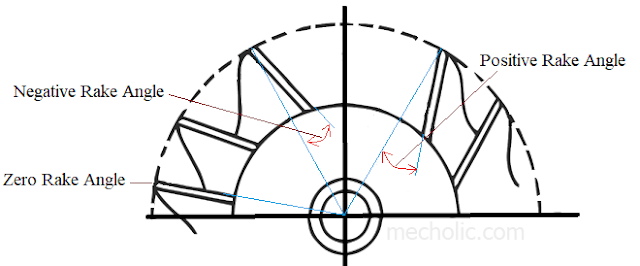
Radial rake angle: it is the angle between the face of teeth and the radial line passing through the cutting edge of the tooth. The radial rake angle may be positive, negative or zero. It is provided free cutting by allowing chips to flow smoothly on the face of the cutter.
Zero rake angle: tooth face and radial line coincide.
Positive rake angle: tooth body and tooth face is the same side of the radial line.
Negative rake angle: tooth surface and radial angle are on opposite side of the radial line.
Axial rake angle: angle between the line of peripheral cutting edge and axis of the cutter. It is an angle in a plane perpendicular to the radial plane.
Clearance angle: it is the angle between the back of the tooth and the tangent to the outside diameter at the cutting edge of the tooth. It is divided into two according to the clearance surface. (primary clearance angle and secondary clearance angle)
Read: Single Point Cutting Tool Geometry
Up Milling and Down Milling Operation - Advantages, Application