Advantages and Application of Neutral, Positive and Negative Rake Angle

Rake angle is one of the significant elements in tool geometry. Proper selection of rake angle enhances the overall efficiency and economy of cutting operation. There are three types of rake angles, namely positive, negative and neutral rake angle. The recommended rake angle depends on tool material, material to be cut, speed and depth of cutting.
 Positive rake angle generally used in the cutting of soft material. It requires less cutting force. However, the higher positive value of rake angle weakens the cutting edge. Fig shows the force acting on a cutting tool with positive rake angle. The force acting on tool tends to shear off the cutting edge of the tool.
Positive rake angle generally used in the cutting of soft material. It requires less cutting force. However, the higher positive value of rake angle weakens the cutting edge. Fig shows the force acting on a cutting tool with positive rake angle. The force acting on tool tends to shear off the cutting edge of the tool.
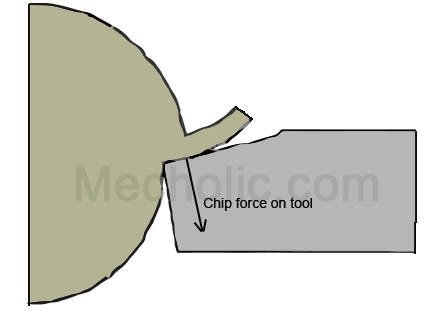 Cutting tool with negative rake angle is stronger and used to cut high-strength material. Fig shows the force acting on the tool. The force directed to the strongest part of the tool.
Cutting tool with negative rake angle is stronger and used to cut high-strength material. Fig shows the force acting on the tool. The force directed to the strongest part of the tool.
Positive rake angle

- Positive rake angle makes the tool sharp and pointed, but reduce the strength of cutting edge.
- It helps the formation of continues chip in ductile material and contributes to avoiding the formation of build-up edge chip.
- HSS tools are typically given a positive rake angle.
- They used in machining of low-strength ferrous and non-ferrous metal.
- Positive rake angle is not preferred to high-speed operation.
Negative rake angle

- Negative rake angle provides greater the strength to cutting edge.
- Negative rake angle prevents adhesion.
- Increase the surface finish.
- Cemented carbide tools are normally given negative rake angle.
- It can be used in the high-speed cutting operation.
- Higher cutting force during machining, this also increases the power consumption.
- Increase vibration, friction and temperature at cutting edge.

